BLEEDING GUMS
Can we ignore the change in saliva color or blood in the sputum after brushing our teeth?
Bleeding gums should not be underestimated or ignored because it usually indicates inflammation of the gums or periodontium, as well as a possible change in general health. Blood on the dental floss usually indicates swelling of the gums. Such signs serve as an alarm for the existence of inflammation around the teeth. It can also be a sign of insufficient massaging and brushing of teeth because harmful bacteria that cause inflammation are retained in dental plaque. Untimely reaction and failure to stop the seemingly insignificant inflammation of the gums will certainly lead to inflammation of the dental apparatus that holds the ligaments to the bone or periodontitis.
The dental appliance consists of elastic fibers that hold the tooth to the bone, thus absorbing the load forces directed towards the teeth. With further spread, the inflammation spreads to the jawbone, breaking down the bone tissue and thus causing mobility, and eventually tooth loss. As a rule, this process is very slow and the patient usually does not feel pain or any symptoms that would refer him to the dentist. Inflammation of the dental apparatus must be cured because a patient with periodontitis will not only lose his teeth but also endanger the health of the entire organism. Numerous studies show that periodontitis develops simultaneously with general diseases such as. diabetes, with which it is closely related. Patients with high blood sugar suffer from periodontitis more than others, and vice versa, periodontitis causes worsening of the disease in diabetics. Periodontitis never comes as an independent problem and we must not view it as an individual and limited problem, because timely treatment of periodontitis reduces the risk of other systemic diseases.
The development and worsening of periodontitis are favored by poor as well as superficial oral hygiene, but periodontitis is also worsened by hormonal changes such as puberty, pregnancy, or general illnesses such as diabetes. Smokers, who represent a special group of patients at high risk for periodontitis, are much more likely to develop periodontitis and the therapy of periodontitis in smokers is significantly slower. Bone and gum breakdown in smokers has a much more aggressive and progressive course compared to non-smokers.
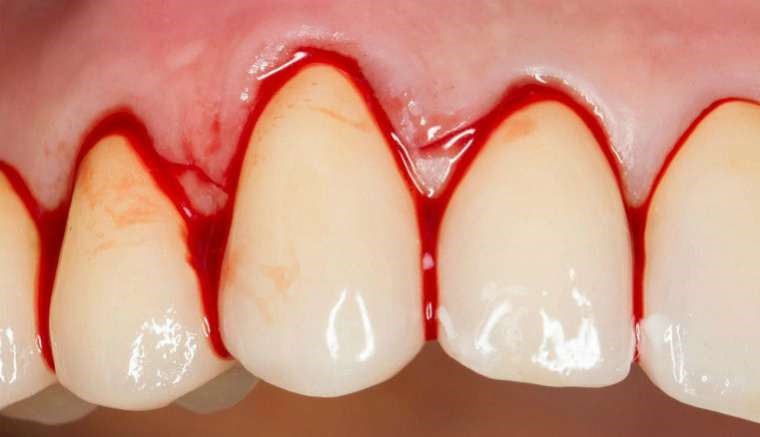
Existing periodontitis can be stopped with systematic treatment, but plaque that is saturated with bacteria on the teeth must be removed. This is achieved by professional teeth cleaning in the dental office. The dentist or dental hygienist must show the patient how to properly monitor and maintain oral hygiene. Of course, it is not enough to just follow the smooth surfaces of the teeth, patients with periodontitis must pay special attention to the interdental spaces as well as to the gums themselves. This is achieved by the use of dental floss and interdental brushes, which are specially designed for cleaning the interdental space. Good and thorough oral hygiene is the key to stopping and preventing gum bleeding. Plaque and bacteria never stick to clean and smooth tooth surfaces, and therefore there is no gum disease.


